1086 Tree Traversals Again (25 分)
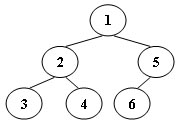
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: “Push X” where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or “Pop” meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
1 | 6 |
Sample Output:
1 | 3 4 2 6 5 1 |
作者: CHEN, Yue
单位: 浙江大学
时间限制: 400 ms
内存限制: 64 MB
代码长度限制: 16 KB
题目大意
给出中序遍历一棵树的过程,求这棵树的后序遍历
分析
一开始没想明白。其实push的顺序就是前序遍历,pop的顺序是中序,知道前序中序,后序就好办了
代码
1 |
|
其他
读取数据的时候,如果cin和getline混用最后一个测试点会段错误,很奇怪,不知道为什么。